Shilpi Gupta Dixit, Veena Bharihoke
Department of Anatomy, University College of Medical Sciences, Delhi - 110 095.
Corresponding Author: Dr. Shilpi G. Dixit, House No. 3164, Sector 23, Gurgaon-122017, Haryana
Email: shilpidr@gmail.com
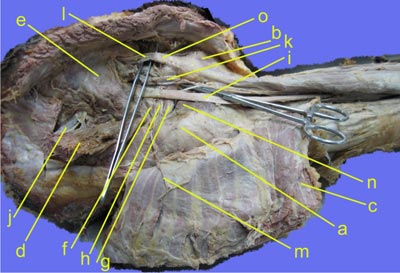
Figure1
Identify the region
Identify the marked structures
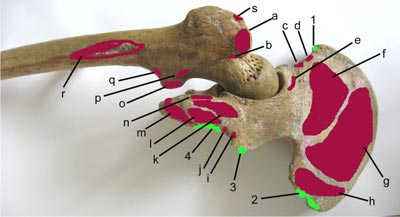
Figure 2
Identify the bones; Identify the structures attached to the areas marked
X-ray of bilateral hands showing peri-articular osteoporosis, a characteristic feature of Rheumatoid arthritis. The small arrow head shows bony erosion.
Figure 1 - The area is gluteal region. The structures are as follows:
a) Greater trochanter
b) Ischial tuberosity
c) Gluteus maximus
d) Gluteal medius
e) Piriformis
f) Superior Gemelli
g) Inferior Gemelli
h) Tendon of obturator internus
i) Sciatic nerve
j) Superior gluteal nerve and vessels
k) Inferior gluteal nerve and vessels
l) PIN structures—from MEDIAL to LATERAL -- Pudendal nerve, internal pudendal vessels and nerve to obturator internus
m) Inferior gluteal nerve
n) Quadratus femoris
o) Sacrotuberous ligament
Figure 2 - The figure is showing posterior aspect of both hip bone and femur.
a) Greater trochanter
a, g) Gluteus medius
b) Obturatus externus
c) Straight head of rectus femoris
d) Sartorius
e) Reflected head of rectus femoris
f) Gluteus minimus
h, r) Gluteus maximus
i) Superior gemellus
j) Inferior gemellus
k) Semimembranosus
l) Semitendinosus & long head of biceps femoris
m) Adductor magnus
n) Quadratus femoris
o) Psoas major
p) Quadratus femoris
q) Iliacus
s) Piriformis
1) Inguinal ligament
2, 4) Sacrotuberous ligament
3) Sacrospinous ligament
Key points to remember
- Gluteus medius and minimus muscles of opposite side steady the pelvis when the foot is raised above the ground during walking. They are also abductors of hip joint, supplied by superior gluteal nerve & vessels
- Paralysis of these muscles makes pelvis unsteady- Trendelenburg’s sign becomes positive. Test may also be positive if head of femur is dislocated or in fracture of neck and shaft of femur.
- If the muscles of right side are paralysed, and foot of left side is raised off the ground, then pelvis of left side sags, and vice versa.
- Gluteus maximus is powerful extensor of hip joint, active while standing from sitting position and climbing stairs, supplied by inferior gluteal nerve and vessels.
- Other small muscles in the gluteal region cause lateral rotation of hip joint.
|


